Regularization:-
Regularization is a technique to discourage the complexity of the model. It does this by penalizing the loss function. This helps to solve the overfitting problem.
Below is the OLS. As the degree of the input features increases the model becomes complex
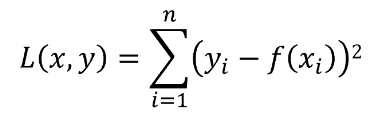
Regularization works on assumption that smaller weights generate simpler model and thus helps avoid overfitting.
L1 Regularization:-
L1 Regularization is also referred as LASSO(Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator).
In L1 norm we shrink the parameters to zero. When input features have weights closer to zero that leads to sparse L1 norm. In Sparse solution majority of the input features have zero weights and very few features have non zero weights.
L1 regularization does feature selection. It does this by assigning insignificant input features with zero weight and useful features with a non zero weight.

In L1 regularization we penalize the absolute value of the weights. L1 regularization term is highlighted in the red box.
Lasso produces a model that is simple, interpretable and contains a subset of input features
L2 Regularization:-
L2 Regularization is also reffered as Ridge Regularization.

In L2 regularization, regularization term is the sum of square of all feature weights as shown above in the equation.
L2 regularization forces the weights to be small but does not make them zero and does non sparse solution.
L2 is not robust to outliers as square terms blows up the error differences of the outliers and the regularization term tries to fix it by penalizing the weights.
Ridge regression performs better when all the input features influence the output and all with weights are of roughly equal size.
Difference between L1 and L2 regularization:-
| L1 Regularization | L2 Regularization |
|---|---|
| L1 penalizes sum of absolute value of weights. | L2 regularization penalizes sum of square weights. |
| L1 has a sparse solution. | L2 has a non sparse solution. |
| L1 has multiple solutions. | L2 has one solution. |
| L1 has built in feature selection. | L2 has no feature selection. |
| L1 is robust to outliers. | L2 is not robust to outliers. |
| L1 generates model that are simple and interpretable but cannot learn complex patterns. | L2 gives better prediction when output variable is a function of all input features and L2 regularization is able to learn complex data patterns |